Content
The principle of operation of an electromagnetic field with a high frequency of electromagnetic oscillations is used in medicine, as physiotherapy, for a simpler explanation, UHF therapy - what it is, you can use the concept of “warming”. Heat treatment is effective as an auxiliary or independent therapy for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, inflammatory processes occurring in body tissues and internal organs. However, for all its usefulness, this procedure is not suitable for everyone and has certain contraindications.
What is UHF therapy
The first therapeutic effect of a pulsed electric field was recorded in Germany in the 30s of the 20th century. To understand UHF therapy - what it is, deciphering this term will help: ultra-high-frequency therapy. The use of specialized equipment during physiotherapeutic methods of influencing the patient’s body is aimed at creating 2 types of electric current (conduction and displacement).
The result of such manipulations is an increase in the permeability of the vascular walls and the flow of cells of the reticuloendothelial system to the inflammatory focus. The thermal effect of ultra-high-frequency therapy is manifested due to the characteristics of body tissues that resist the penetration of electric current. The procedure during which a device for UHF therapy is used is called EVT therapy (stands for eddy current electrode).
Mechanism of action
The main element of the device for UHF therapy is an ultra-high-frequency generator that reproduces ultra-high-frequency waves. Both stationary and portable equipment are used to carry out physical procedures. The power of exposure is adjusted according to the patient’s thermal sensations (indication occurs by the intensity of the glow of a neon lamp placed in the UHF field and the deflection of the milliammeter arrow).
To supply electromagnetic waves to the patient, capacitor electrodes are used, which are metal disks in an insulating shell connected to a generator. The dosage of heat during ultra-high-frequency therapy is calculated according to the instructions, based on the intended purpose of treatment, and can be of the following types:
|
Dose (intensity of heat sensation during UHF therapy) |
Output power for portable devices, W |
Output power for stationary devices, W |
Application of therapy |
|
Athermic (no) |
Anti-inflammatory |
||
|
Oligothermic (light) |
Improving cell nutrition |
||
|
Thermal (clear) |
Normalization of metabolism |
||
|
Expressed |
Provocative effect |
Benefits and harms
Knowing the principle of action and understanding UHF therapy - what it is, we can conclude that treatment methods using UHF have a beneficial effect on the human body. Ultra-high frequency current can influence processes occurring in nerve tissues, bones, tendons and joints. The effectiveness of using a field with a high frequency of electromagnetic waves is used to treat acute inflammatory diseases, neuroses, metabolic disorders, and problems with the spine.

The effect of such a physiotherapeutic procedure may be exactly the opposite of what was expected if you do not adhere to the basic rules of its implementation. Too much heat between the capacitor plates may cause skin burns. A danger to the patient's health during UHF is intense heating of the inflamed area, due to the fact that the proliferation of pathogenic cells increases under the influence of heat. The feeling of discomfort during such a procedure should be a reason for the physiotherapist to reduce the frequency of oscillations of electromagnetic waves.
Indications
A referral for the procedure must be written by a qualified doctor who is familiar with the patient’s medical history and knows the patient’s body’s reactions to irritants. UHF physiotherapy is carried out as part of a course of treatment for the following problems:
- inflammatory diseases;
- injuries of spinal and peripheral nerves;
- radiculitis;
- eye diseases;
- polio;
- thrombophlebitis;
- diseases of the digestive and genitourinary systems;
- ENT diseases;
- skin diseases;
- exacerbation of inflammatory processes in bone tissue (in dentistry).
Contraindications
Conducting UHF therapy can be dangerous for the body of patients who have pacemakers, implants and other foreign metal objects. In addition, doctors do not prescribe UHF in the following cases:
- diagnosed blood diseases, thyrotoxicosis;
- there are neoplasms;
- during a feverish state;
- the patient suffers from cardiovascular failure;
- during pregnancy;
- medical history includes uterine fibroids, mastopathy, orchiepididymitis;
- before surgery;
- low sensitivity to the effects of electromagnetic waves.

Side effects
- increase in temperature during therapy or immediately after it;
- deterioration of health;
- skin burn;
- internal bleeding.
UHF treatment
Before starting UHF therapy, the specialist selects the size and shape of the plates depending on the location of the area that needs to be treated. Electrode holders are treated with an alcohol-containing solution and brought to the patient. The furniture on which the patient is placed must be wooden. Depending on the frequency of wave oscillations, the technique uses continuous or pulsed UHF therapy. The dosage of heat is set based on the readings indicated in the direction.
For sinusitis
Acute and chronic forms of sinusitis and sinusitis respond well to high-frequency waves. UHF for sinusitis is the final stage of the treatment course and is carried out for 10-15 days (depending on the depth of the location of purulent formations in the maxillary sinus). The duration of one procedure is from 10 to 15 minutes. The positive effect of UHF therapy is achieved by reducing swelling under the influence of diadynamic current.
For bronchitis
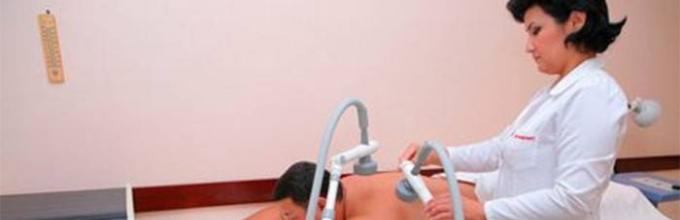
Treatment of diseases of the bronchopulmonary system using UHF aims to strengthen the walls of the alveoli and stop inflammatory processes. The procedure involves placing the UHF device plates on the chest parallel to the patient’s body (as in the photo). The distance between the electrodes is no less than the diameter of the plate, selected according to the size of the patient’s lungs. A UHF course for bronchitis lasts from 6 to 12 sessions twice a day, lasting from 5 to 20 minutes.
For otitis media
The UHF procedure for otitis should be carried out under the supervision of a physician, due to the fact that the electromagnetic field can provoke the production of fluid in the middle ear cavity. To monitor the body's response to UHF exposure, the course of physiotherapy at the initial stage is no more than 6 procedures of 5 minutes each. In the absence of pathologies, the duration of treatment is increased to 10 days. The location of the electrodes during UHF therapy is as follows: one plate is at the mastoid process of the temporal bone behind the ear, the other is in the temple area.

How to replace UHF at home
If it is not possible to carry out physical procedures in a hospital, you can purchase a portable device that can be used to carry out UHF therapy at home. Before warming up, it is necessary to ensure that the home appliance is safe to use. It should be remembered what the UHF procedure is and that it involves interaction with high frequency current. It is better to seek help from relatives in order to correctly install the electrodes with a gap of 3 cm. Self-medication should be done carefully, and only after consulting a doctor.
Video
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!Discuss
Physiotherapeutic UHF procedure - indications, mechanism of action and what to replace at home
Initially, ultra-high-frequency exposure was determined to be negative. People exposed to radiation said they felt worse and got sick more often. Subsequently, it was discovered that high-frequency waves at the right intensity have a therapeutic effect. The method became widespread in the mid-twentieth century in Germany. Today, UHF therapy involves working with different frequencies: low power - up to 30 W and high power - over 150 W.
The best results are obtained by therapy using pulsed UHF exposure. The duration of exposure to one pulse is usually from 2 to 8 seconds. Under the influence of electric current, tissues heat up, blood supply improves, and capillary permeability increases. UHF treatment is suitable during the rehabilitation period, when the body does not have enough of its own strength to recover and requires additional stimulation. UHF is most effective in the treatment of respiratory diseases. Physiotherapy based on ultra-high-frequency effects helps get rid of chronic rhinitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Mechanism of action of UHF
The method is based on the effect of an electromagnetic field, which absorbs heat from damaged tissues. During the heating process, blood supply and lymph flow increase. This helps relieve inflammation and restore diseased tissues.
The dosage of UHF waves is determined based on the patient’s condition and his subjective feelings. In the process of UHF exposure, physical and chemical processes in the tissues of the body change. This physiotherapeutic method has a beneficial effect on the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and bone tissue.
During the procedure, capacitor plates are applied to the patient. Their size varies: small plates are used to treat rhinitis, sinusitis and other diseases. Large plates are often used in spine treatment.
When treating with UHF devices, safety precautions must be observed. If the procedure is violated, burns and electrical damage may occur.
Indications
This method is recommended as an auxiliary component of general therapy. UHF exposure has demonstrated the greatest effectiveness in the fight against diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes. Indications for UHF therapy include:
- gynecological diseases - adhesions, inflammation of the appendages, candidiasis, etc.;
- pathology nervous system– neuralgia, cerebrovascular accident, meningitis, encephalitis, insomnia, concussion;
- cardiovascular disorders - hypertension, Raynaud's disease, atherosclerosis, varicose veins;
- ENT diseases – bronchitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis, bronchial asthma;
- diseases of the digestive system - gastritis, enteritis, pancreatitis, esophagitis, cholecystitis, viral hepatitis, gastric ulcer;
- skin diseases - psoriasis, abscess, boils, trophic ulcers, phlegmon, acne;
- eye diseases – glaucoma, barley, blepharitis;
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system - arthritis, radiculitis, dislocations, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis;
- dental diseases – gingivitis, periodontitis, alveolitis, ulcerative lesions.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on many factors. When prescribing therapy, not only the patient’s diagnosis is taken into account, but also his age, general condition and the presence of concomitant factors. UHF is one of the few methods that can be used during an acute inflammatory process. UHF therapy is recommended during the rehabilitation period, when there is a high probability of re-infection and the development of complications.
Contraindications
UHF therapy is prohibited during pregnancy, bleeding disorders, the presence of tumors, venous thrombosis, and the presence of a pacemaker. Contraindications to UHF are also:
- third stage hypertension,
- fever,
- ischemic disease,
- persistent angina.
Procedures are performed with caution for those who have metal implants. The procedures are not recommended for people with low blood pressure, diffuse toxic goiter, or thyroid pathologies.
UHF therapy or ultra-high frequency therapy is one of the methods of treatment and prevention of many diseases, which is based on the effect on the human body of a continuous or pulsed electric field. The wavelength is in the range from 10 to 1 meter, and the oscillation frequency is from 30 to 300 MHz.
During the procedure, the effect on body tissue occurs through capacitor plates, which are connected to a generator of ultra-high-frequency oscillations. In this case, the area of the body located directly in the zone of influence of the device is completely penetrated by the healing energy of the electric field.
Application
Numerous studies have revealed that the procedure has a complex and diverse effect on the human body.
- noticeable inhibition of the activity of pathogenic bacteria;
- activation of blood circulation, as well as lymph circulation at the site of the disease;
- an increase in the concentration of calcium ions in the pathological focus;
- activation of bile secretion;
- expansion of capillaries;
- normalization of blood pressure;
- activation of blood circulation in the kidney area;
- decreased secretion of bronchial glands;
- stimulating the formation of a barrier from the body’s connective tissue;
- an action aimed at relieving spasms of the smooth muscles of the stomach, gallbladder and intestines.
 Thus, UHF therapy is effectively used in the treatment of such pathologies.
Thus, UHF therapy is effectively used in the treatment of such pathologies.
- Inflammatory processes, both acute and subacute, of teeth, ears, eyes and tonsils.
- Inflammatory processes of an acute nature, as well as suppuration in human systems and organs.
- Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs.
- Diseases of the nervous system, as well as injuries. These include radiculitis, causalgia, phantom pain, neuralgia, and plexitis.
- Vascular diseases, for example, thrombophlebitis.
- Bedsores, wounds that do not heal for a long time, frostbite.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Polio.
- Vegetovascular dysfunctions.
- Encephalitis.
Contraindications
The procedure is contraindicated in patients with the following pathologies:
- fever;
- malignant neoplasms;
- blood diseases and bleeding;
- purulent processes;
- aortic aneurysm;
- adhesive disease;
- heart failure of II and III degrees;
- a condition characterized by low blood pressure - hypotension;
- myocardial infarction;
- active phase of pulmonary tuberculosis;
- the presence of a pacemaker in the area of operation of the device;
- pregnancy.
Important: the procedure is performed with extreme caution on patients with dentures and metal objects in the body.
Mechanism of action
 The nature of the propagation of the electric field depends on which capacitor plates are selected, their shape and size, as well as their location on the patient’s body.
The nature of the propagation of the electric field depends on which capacitor plates are selected, their shape and size, as well as their location on the patient’s body.
The final result of the procedure is determined by the dosage of heat used for therapy.
- Athermal dosage – no heat is felt. Used to eliminate foci of inflammation.
- Oligothermic dosage – little heat is felt. Used to normalize metabolic processes.
- Thermal dosage – the patient feels the heat well. Used to increase inflammation.
Throughout the procedure, the patient is in a comfortable position. The plates are placed on the damaged area of the body. The arrangement of the plates can be longitudinal, transverse or at an angle. The distance between the plates should not exceed their diameter.
In order to achieve the deepest penetration of the electric field and impact on the pathology site located deep in the tissues, a transverse method of attaching plates to the patient’s body is used.
If the pathological process occurs on the surface of the body, the plates of the device can be attached longitudinally.
Note: most often, specialists use the transverse method of fastening capacitor plates.
For the procedure to be as effective as possible, a small amount of space should remain between the surface of the body and the plate. air space. The size of the gap can be determined by knowing the depth of the lesion.
If the procedure is performed on children or adolescent patients, it is important to correctly determine the power of the effect on the body. In this case, it is necessary to maintain an air gap, for which special circles made of flannel or felt, with a thickness of one to three centimeters, are used.
Note: UHF therapy can be performed on children from the first days of life.
Procedures are usually carried out daily lasting from 8 minutes to a quarter of an hour. The full course includes from 5 to 15 procedures.
Benefits of the procedure
 Under the influence of the emerging electric field, a slight movement of ions begins, which leads to transformation electrical energy to thermal. From a medical point of view, this phenomenon is called the thermal effect.
Under the influence of the emerging electric field, a slight movement of ions begins, which leads to transformation electrical energy to thermal. From a medical point of view, this phenomenon is called the thermal effect.
Heating of tissues affects such body processes as:
- metabolism;
- circulation;
- enzyme activity.
The nervous system reacts most strongly to the procedure. Oligothermic dosage of heat, that is, during the procedure the heat is felt insignificantly, but it has a stimulating effect on the nervous system. While thermal dosage, when heat is pronounced, the activity of the central nervous system is inhibited.
This type of therapy also affects blood vessels. Treatment allows you to reduce vascular tone and slightly expand the capillaries. In addition, blood pressure is normalized, blood flow and outflow of venous blood are increased.
Therapy promotes changes in chemical processes: the content of leukocytes and erythrocytes in the blood increases. Thus, it is possible to achieve rapid formation of a protective barrier in the area of inflammation. This is especially important if we're talking about about inflammation that is purulent in nature.
As a result of the effect on the stomach, gall bladder, intestines and bronchi, an antispastic effect occurs, the motor and secretory functions of the stomach are activated. The activity of the kidneys and the secretion of bile are activated.
Many metabolic processes in the body are normalized, in particular protein and carbohydrate. The process of oxygen supply to tissues improves, thus reducing and oxidative processes occur faster.
In general, UHF therapy has a complex effect on the human body, expressed in the dilation of blood vessels, elimination of inflammatory processes and swelling, destruction of bacteria and prevention of spasms.
UHF therapy is a common physiotherapeutic procedure that many have probably encountered. In this article we will tell you what it is, when it is prescribed, how it works for a particular disease, and who should not use this method for treatment.
UHF therapy (ultra-high frequency therapy) is used in physiotherapy and is based on the use of ultra-high frequency electromagnetic fields. Essentially, this is heat treatment that penetrates deep into organs and tissues using special equipment. One of the significant advantages of this method is that the use of UHF therapy is possible for fresh fractures and acute inflammatory processes. These conditions are a contraindication to most physiotherapeutic treatments.
UHF promotes:
- acceleration of regenerative processes, including healing of fractures and tissue damage;
- reducing swelling;
- activation of central and peripheral circulation;
- reducing pain sensitivity;
- inhibition of the activity of pathogenic bacteria;
- elimination of inflammatory processes;
- strengthening of proliferative processes of connective tissue elements;
- increasing the efficiency of immunological reactions.
Ultra-high frequency electromagnetic fields were first used as a treatment method in Germany in 1929. The invention of the apparatus and method was prompted by complaints from radio station personnel about the negative effects of radio waves on health.
Biophysical mechanism
Due to the long length of electromagnetic waves and high frequency, they penetrate deeply into tissues, where conduction currents arise, and the effect occurs at the level of cell membranes and at the subcellular level. With this effect, the electric part of the electromagnetic field (85%) prevails over the magnetic one.
The effect of the UHF electric field (EF) consists of non-thermal (oscillatory) and thermal components. The greatest absorption of UHF EF energy and heat generation occurs in dielectric tissues (skin, nervous, bone, connective, adipose tissue). Less absorption of UHF EF energy and heat generation occurs in well-conducted media: blood, lymph, urine and in well-supplied tissues.
A distinctive feature of UHF EP is that it operates at a distance, without contact of electrodes with the patient’s body, which makes it possible to influence deep-lying organs and tissues that are inaccessible to influence by other devices.

Mechanism of action and equipment for the procedure
The mechanism of action of the procedure is based on two effects:
- oscillatory, characterized by changes in the biological structure of cellular elements at the molecular and physicochemical levels;
- thermal, leading to heating of tissues when ultra-high frequencies of the EM field are converted into thermal energy.
When interacting with the electromagnetic field generated by the physiotherapeutic device and the patient’s body, 2 types of electric current are generated.
- In anatomical structures characterized by high electrical conductivity (lymph, blood, urine and tissues with good blood supply), charged particles oscillate with the frequency of a given field and a conduction current arises in the tissues. Since particles vibrate in a viscous medium, energy absorption develops, which is associated with overcoming the resistance of this medium. Energy absorption is called ohmic loss. The energy absorbed by tissues is released as heat.
- In tissues that are close in their electrical properties to dielectrics (nervous, fatty, connective, bone), dipoles are formed - polar molecules that change their orientation with the frequency of vibration of the high-frequency field. The rotation of dipole particles in dielectrics leads to the formation of a displacement current, and the losses that are associated with the particles overcoming a viscous medium are called dielectric losses.
When exposed to UHF, the displacement current predominates - the field penetrates deeply, almost without loss, into tissues that do not conduct electric current well. The main heat release is realized due to conduction currents.
A classic UHF therapy device is equipped with a high-frequency generator, electrodes, which are an electrical conductor, inductors that create a magnetic flux, and emitters. The devices are stationary (“UHF-300”, “Impulse-2”, “Impulse-3”, etc.) and portable (“UHF-30”, “UHF-66”, “UHF-80”, etc.). All of them are classified by power: low power up to 30 W, medium - UHF up to 80 W and high power up to 350 W.
Therapeutic effect of UHF therapy
When exposed, a wide range of local and general reactions of the body are formed:
- effect on the nervous system: stimulating at low-heat dosages; inhibition at thermal dosages, stimulating effect of the parasympathetic nervous system; reducing sympathicotonic effects on internal organs, which has an analgesic effect;
- trophic effect- due to the expansion of capillaries, the appearance of collaterals, increased vascular permeability, improved lymphatic drainage;
- antispasmodic effect on the smooth muscles of hollow organs, bronchi, vascular walls;
- proliferative-regenerative effect by activating the function of connective tissue, improving tissue trophism;
- anti-inflammatory effect due to tissue dehydration, increasing the number of lymphocytes and increasing their phagocytic activity, bacteriostatic effect;
- stimulating effect on the endocrine system– thyroid gland and adrenal cortex;
- normalization of motor and secretory function stomach and intestines.
Ultrahigh-frequency therapy is practically the only method of physiotherapy that is not contraindicated in the acute phase of inflammation.
Mechanism of action in the treatment of various pathologies
- As mentioned above, UHF is used for acute inflammation. With the development of the inflammatory process at the site of the outbreak, an inflammatory infiltrate is formed due to the accumulation of blood cells and lymph. The procedure is precisely aimed at resolving the inflammatory infiltrate. During the session, the concentration of calcium ions in the area of the procedure increases, which leads to the formation of connective tissue near the source of inflammation and prevents further spread of infection. An increase in the permeability of capillary walls leads to increased entry into the site of inflammation of immune bodies and protective cells of the reticuloendothelial system. But in the presence of purulent inflammation, the technique is permissible only if there are conditions for drainage of pus from the affected area.
- When treating infectious processes of the upper and lower respiratory tract, an inhibitory effect on the vital activity of microbes is noted. An analgesic and immunostrengthening effect develops, favorable conditions are created for the regeneration of affected tissues and the risk of complications is reduced. The expansion of capillaries and a significant improvement in the permeability of the vascular wall leads to an increase in the body's susceptibility to drugs. Activation of phagocyte cells helps to more actively fight infection.
- In the treatment of cardiovascular pathologies, the procedure is prescribed primarily to develop a vasodilator effect. Leads to improvement of central and peripheral blood circulation. There is an improvement in myocardial contractile function. Reducing the increased tone of the vascular wall leads to a decrease in blood pressure. Amelioration of the venous outflow occurs, and the capillaries significantly expand. After the procedure, tissue swelling associated with dysfunction is reduced of cardio-vascular system.
- Use for diseases of the digestive system provides a general strengthening effect on the body, reducing pain and eliminating spasms. An anti-inflammatory effect is realized and tissue healing processes are accelerated, which is relevant in the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers. After the procedure, there is an increase in motor and secretory function - improvement in intestinal motility and bile secretion.
- The procedure, indicated as part of the auxiliary treatment of genitourinary diseases, leads to the elimination of the inflammatory reaction, reduction of swelling, improvement of blood circulation and healing of affected tissues.
- When treating diseases of the nervous system, an analgesic effect develops by inhibiting the development of pain in the brain. Blood circulation improves, which leads to faster healing and regeneration of nerve tissue. There is an improvement in the conduction of nerve impulses. The tone of the sympathetic nervous system decreases and the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system increases.
- When treating eye diseases, microcirculation in the mucous layer of the eyes and eyelids improves. Antiallergic and anti-inflammatory effects are realized, phagocytosis reactions are enhanced, which accelerates the processes of tissue regeneration and healing.
- When treating gum diseases, there is an improvement in blood circulation and the viability of bacteria is inhibited. Painful sensations are significantly reduced.
- UHF for fractures is used from 2-3 days after applying plaster, has an analgesic effect, helps reduce tissue swelling, accelerates the process of formation of primary callus and bone tissue regeneration in general. Helps eliminate muscle spasms.
- The procedure takes on particular importance in the rehabilitation period after operations and diseases: microcirculation improves and a network of collateral vessels is formed, which leads to an acceleration of the regeneration process of affected tissues. UHF therapy reduces the risk of infection of a postoperative wound, since it inhibits the vital activity of pathological microorganisms that can cause suppuration. In general, the procedure helps activate the body’s defenses and has an analgesic effect, which facilitates the healing process.
The effectiveness of treatment with UHF depends on the stage and severity of the disease, the duration of exposure and the range of electromagnetic vibrations, the location of the procedures, the individual sensitivity of the patient and the use of other treatment methods.

The indications are:
- purulent-inflammatory diseases of the skin and subcutaneous fat;
- acute and subacute stages of inflammatory diseases of internal organs;
- diseases of the peripheral nervous system of an inflammatory, dystrophic and traumatic nature;
- diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system;
- frostbite;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- allergic diseases;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- arterial hypertension stages I - II;
- inflammatory diseases in dentistry;
- postoperative conditions;
- trophic ulcers, bedsores.
Indications for UHF procedure
The purpose of treatment, parameters and duration of the procedure depend on:
- patient's age;
- stage and course of the existing disease;
- general condition;
- concomitant diseases;
- the presence of restrictions and contraindications for the procedure.
The procedure is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- ENT organs and respiratory system: bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, bronchial asthma, bronchiectasis, tonsillitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, pansinusitis, otitis media, laryngitis and tonsillitis;
- cardiovascular system: hypertension stages 1 and 2, obliterating endarteritis, cerebral circulatory disorders, varicose veins;
- musculoskeletal system: radiculitis, arthritis and polyarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis, dislocations, bruises, bone fractures, osteomyelitis;
- digestive organs: gastritis, esophagitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, pancreatitis, viral hepatitis, hepatocholecystitis, cholecystitis, enterocolitis, colitis, constipation, paraproctitis;
- genitourinary system: nephritis, epididymitis, pyelonephritis, salpingitis, cystitis, endometritis, oophoritis, salpingoophoritis, prostatitis, mycoplasmosis, candidiasis;
- nervous system: neuralgia, neuritis, migraine, phantom pain, insomnia, plexitis, sciatica, spinal cord and brain injuries, encephalitis, causalgia, Raynaud's disease, polyneuritis;
- skin: boils, carbuncles, abscesses, streptoderma, neurodermatitis, herpes simplex, trophic ulcers, eczema, psoriasis, acne, hidradenitis, dermatitis, felon, burns, frostbite, phlegmon, wounds, including purulent, bedsores;
- organs of vision: glaucoma, conjunctivitis, eyelid abscess, burns, uveitis, barley, scleritis, blepharitis;
- in dentistry: gingivitis, alveolitis, ulceration of the oral mucosa, periodontitis, periodontitis, burns, injuries;
- in the postoperative period: postoperative infiltrates and wounds;
- rehabilitation after injuries and illnesses.
general characteristics
For therapy, high-frequency EP is used with a frequency of 27.12 MHz, with a wavelength of 11.05 m (in domestic and foreign devices) and 40.68 MHz, with a wavelength of 7.37 m (in domestic devices). The power used ranges from 5 W to 350 W in continuous mode and 18,000 W in pulse mode.
Low intensity of the UHF field is used in the exudative stage of inflammation, and high intensity - in the proliferative stage of the inflammatory process, always after drainage of the exudate.
Basic impact scheme
To supply UHF EP, rigid and flexible paired capacitor plates (electrodes) are used. different sizes. During the procedure, a longitudinal (to influence superficial tissues) and transverse arrangement (to influence deeper tissues) of two capacitor plates is used.
It is necessary to ensure that the distance between the plates is greater than the size of the plates themselves. With shallow exposure, the gap between the plates and the skin is 1 - 2 cm, with deep exposure - 3 - 4 cm, in total from two plates no more than 6 cm.
Dosimetry of EP UHF
UHF therapy is dosed according to the power of the device, non-thermal (athermic), low-thermal (oligothermic), thermal (thermal) and high-thermal doses are used, focusing on the readings of the devices and the patient’s sensations - the feeling of warmth. Be sure to check the resonance of the technical and therapeutic oscillatory circuit.
Pulsed UHF therapy
During the procedure of pulsed UHF therapy, tissue is exposed to UHF EP in the form of individual pulses with a duration of 2 to 400 μs, with a frequency of 50 – 800 Hz. The pause is 1000 times longer than the pulse, which allows you to increase the pulse power. Thus, the pulse power of domestic devices reaches 18 kW, and in foreign ones it is no more than 150 W.

Therapeutic effects of pulsed UHF EP:
- inhibitory effect on the central nervous system;
- pronounced antispasmodic effect;
- analgesic effect;
- trophic effect;
- metabolic effect;
- anti-inflammatory effect.
A course of treatment
The duration of one procedure does not exceed 10 - 15 minutes once a day, with a non-thermal technique - twice a day, the course is 5 - 12 procedures. If necessary, it is recommended to repeat the course no earlier than after 8-10 weeks; it is advisable to repeat the procedure no more than 2 times a year.
UHF - pros and cons
This type of physical therapy can be beneficial or cause serious harm. The decisive factor is whether UHF of the chest or other part of the body is done by a specialist or not. Self-medication is unacceptable. If the power is calculated incorrectly, serious complications can arise. The negative consequences of UHF in physiotherapy are as follows:
- thermal tissue damage due to contact with electrodes;
- bleeding caused by hyperthermia;
- electric shock (occurs in case of contact with exposed areas of the device);
- scars appear.
Rules for the use of UHF therapy techniques
Basic principles of UHF therapy:
- not prescribed during the remission phase of inflammation;
- not prescribed before and immediately after surgical interventions, due to the risk of causing bleeding;
- do not prescribe to a purulent focus without prior drainage;
- the more acute the inflammation, the lower the UHF dose should be;
- promotes the rapid formation of granulation tissue in the wound, which can lead to the formation of scars;
- for inflammatory diseases it is prescribed in a short course of 4–5 procedures;
- do not use in postoperative patients with drainages through which fluid flows due to the risk of burns;
- not prescribed to patients with pneumosclerosis, with chronic hyperplastic processes in the lungs and ENT organs;
- must be prescribed before the Ural Federal District;
- do not carry out in the presence of metal structures in the affected area;
- prescribed only after puncture of the sinuses for purulent sinusitis;
- not prescribed for epitympanitis; for mesotympanitis - only if there is good outflow in a hospital setting;
- not carried out in the area of the heart, in order to avoid disturbances in its rhythm.
How to replace UHF at home
If it is not possible to carry out physical procedures in a hospital, you can purchase a portable device that can be used to carry out UHF therapy at home. Before warming up, it is necessary to ensure that the home appliance is safe to use. It should be remembered what the UHF procedure is and that it involves interaction with high frequency current. It is better to seek help from relatives in order to correctly install the electrodes with a gap of 3 cm. Self-medication should be done carefully, and only after consulting a doctor.
Side effects of therapy
If the rules for using methods and safety precautions are not followed, undesirable side effects may occur:
- burns occur due to wet dressings, exudate, metal objects, metal structures entering the affected area;
- bleeding may occur when using UHF EP before or after surgery due to increased blood supply to tissues;
- scars arise as a result of excessive development of connective tissue under the influence of UHF EP;
- Electric shock occurs in rare cases when the device malfunctions or safety precautions are not followed (touching the device body, wires, radiators during the procedure).
Contraindications to the UHF procedure
Among the absolute contraindications to the procedure:
- cardiovascular failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- hypertension stage 3;
- persistent angina;
- fever;
- malignant tumors;
- the patient has a pacemaker;
- venous thrombosis;
- foreign metal bodies in the body more than 2 cm (for example, an implanted joint prosthesis).
Expectant mothers are wondering whether UHF can be performed during pregnancy. The answer is clear - no, this is an absolute contraindication to the procedure.
Relative contraindications to therapy are benign tumors, hyperthyroidism and the presence of metal objects no more than 2 cm (metal dentures).
UHF therapy for children

UHF therapy is allowed to be used for children from the first days of life. When applying capacitor plates, they must be fixed with bandages. Only non-thermal or low-thermal dosages are used.
UHF dosimetry in children depends on age: 0 - 1 year - no more than 15 W, from 1 to 3 years - no more than 15 - 20 W, from 3 to 7 years - no more than 30 - 40 W, over 7 years - up to 50 – 60 W. Exposure time to UHF EF is from 5 to 15 minutes. depending on age.
Methodology
The procedure is performed in the physiotherapy department. There is a separate cabin with a wooden daybed. The patient is in a lying or sitting position, depending on the location of the affected area and general condition. You don’t have to take off your clothes - electromagnetic fields easily penetrate fabric and even plaster.
Electrodes are selected individually depending on the area of the diseased area of the body. There are two types of capacitor electrodes:
- plate-discs made of metal and coated with insulating material;
- rectangular soft plates with an area of up to 600 cm.
The plates are installed in special holders, treated with a disinfectant solution and brought to the site of exposure.
Installation of electrodes is carried out in two ways:
- transverse;
- longitudinal.
With the transverse installation method, the electrodes are placed opposite each other, with one plate installed on the projection of the diseased area, and the second on the opposite side.
This arrangement of the electrodes ensures the penetration of the electromagnetic field through the entire body of the patient. Those. In addition to the local, there is also a general effect. The distance between the body and the electrode should not be less than 2 centimeters.
With the longitudinal installation method, the electrodes are applied only to the diseased part of the body. This method is most relevant in the treatment of superficial diseases, since in this case the electromagnetic fields do not penetrate very deeply. The space between the electrodes and the body should be no more than 1 centimeter.
As for the installation of electrodes relative to the diseased area, the principle is this: the closer the plate is to the affected area, the stronger the thermal effect will be. It is also important to follow safety rules - if the electrodes are placed incorrectly, burns can occur.
After the electrodes are installed on the body, the device (generator) is turned on and a certain electric current power is set, at which the patient receives a therapeutic dose of UHF. The electromagnetic field power is adjusted using a special regulator located on the generator control panel.
The patient's sensations and effect depend on the dose rate:
- Thermal dose (100-150 W). A provocative effect in which a person feels pronounced heat in the area where the electrodes are installed.
- Oligothermic dose (40-100 W). Cellular nutrition, blood circulation and metabolism improves. Thermal sensations are insignificant.
- Athermic dose (15-49 W). Pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. The patient does not feel any thermal effects.
Depending on the selected dose of UHF fields, the following changes develop in the body, which we wrote about above (increased phagocytic activity of leukocyte cells, activation of fibroblast function, stimulation of metabolic processes, and others).
The duration of the session for adult patients is 10-15 minutes. The course includes 5 to 15 procedures, which are performed every other day or daily.
Features of UHF for children
The procedure can be performed on children of any age, including newborns a few days after birth, but no more than 2 courses per year. Most often, indications for UHF are diseases of the ENT organs and upper respiratory tract - they are prescribed for sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammatory processes. During the session, devices with low power and low-thermal dosage are used:
- for children under 7 years of age - dose rate no more than 30 W;
- children 7-16 years old - dose rate no more than 40 W.
For children under 5 years old, electrodes are installed on the affected area, and instead of an air gap between the electrode and the skin, a special bandage is placed to prevent burns.
- 0-6 months: up to 5 minutes;
- 6-12 months: up to 7 minutes;
- 12 months – 7 years: up to 8 minutes;
- children from 7 years old: 10 minutes.
UHF therapy has a wide range of applications for various diseases.
On the projection of the tonsils
Small-diameter electrodes are placed on the anterolateral surfaces of the neck, in a position with the head thrown back. The required gap is 1.5 - 2.5 cm, oligothermic dose, exposure time 7 - 15 minutes, course 5 - 12 procedures.
To the tracheal area
Medium-diameter electrodes are placed: one in the area of the middle third of the sternum, the second in the area of the upper third of the sternum. The required gap is 2.5 - 3 cm, oligothermic dose, exposure time 10 - 15 minutes, course 5 - 12 procedures.
To the lung area
The electrodes are placed transversely at the level of the pulmonary roots: one on the anterior and the other on the posterior surface of the chest or in front or behind the lesion on the affected side. The required gap is 3 - 3.5 cm. They start with an athermic dose and gradually increase it to an oligothermic one, exposure time is 12 - 15 minutes, a course of 5 - 12 procedures.
To the area of the paranasal sinuses
Electrodes are placed on the projection area of the frontal and maxillary cavities. The required gap is 1.2 - 2 cm, the dose is oligothermic, the exposure time is 5 - 15 minutes, the course is 5 - 12 procedures. A prerequisite is UHF after piercing the sinuses.

UHF - indications and contraindications
This manipulation has a wide range of applications. At the same time, the UHF procedure has a considerable list of contraindications. Before performing it, you need to weigh all the positive and negative features. Only a doctor can do this accurately. Self-medication is dangerous! Even if the procedures are performed at home, they must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
UHF therapy - indications

When prescribing this therapy, the doctor takes into account the following factors:
- patient's age;
- intensity of disease manifestation;
- concomitant diseases;
- presence of contraindications to the procedure.
UHF therapy is used to combat inflammation that is in the active stage. During this period, an infiltrate is formed in the body due to the accumulation of lymph and blood cells. UHF therapy promotes its resorption. The amount of calcium ions increases in the problem area. As a result, connective tissue forms around the lesion: it serves as a barrier that prevents the spread of infection. However, this method of physiotherapy can only be used in cases where pus drains from the area affected by inflammation.
UHF indications for implementation are as follows:
- ENT diseases
(bronchitis, frontal sinusitis, otitis media, sinusitis, and so on) – the procedure inhibits the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms. At the same time, such physiotherapy strengthens the immune system and has an analgesic effect. In addition, UHF accelerates the healing process of affected tissues and minimizes the likelihood of complications. - Gastrointestinal pathologies
(pancreatitis, ulcers, enteritis, cholecystitis, viral hepatitis) – the procedure reduces pain, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and accelerates tissue healing. In addition, UHF improves intestinal motility. - Disorders in the nervous system
(plaxitis, neuritis, encephalitis, migraine, sciatica) – thanks to the acceleration of blood circulation, tissues are restored faster. At the same time, muscle spasms are reduced. - Eye diseases
(blepharitis, uveitis, glaucoma, etc.) – this procedure reduces allergies and has an anti-inflammatory effect. Also, under its influence, phagocytosis increases, due to which damaged tissues are restored faster. - Diseases of the cardiovascular system
(hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, varicose veins) – after UHF, tissue swelling decreases, muscle tone decreases and, as a result, blood pressure normalizes. - Skin diseases
(acne, eczema, psoriasis, phlegmon, herpes) - this procedure strengthens the body’s defense system, accelerates the process of epithelization and has a desensitizing effect. - Dental problems
(alveolitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, trauma) – UHF increases blood circulation in the gums and reduces pain. In addition, this procedure inhibits the viability of pathogenic bacteria. - Pathologies of the musculoskeletal motor system
(dislocations, fractures, bruises, radiculitis, and so on) - during this physiotherapy, the tissues are heated, due to which the blood vessels dilate and, as a result, blood circulation increases. This improves cell nutrition and accelerates their regeneration. - Rehabilitation in the postoperative period
– the procedure reduces the risk of tissue infection and complications. In addition, it accelerates the regeneration process, relieves pain and strengthens the body's defenses.
UHF – contraindications
In some cases, this procedure cannot be carried out. UHF treatment is prohibited under the following circumstances:
- pregnancy;
- blood clotting disorder;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms;
- stage 3 hypertension;
- fever;
- presence of a built-in pacemaker;
- angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- severe blockage of veins.
Algorithm
The nurse must strictly follow the doctor's orders. The effectiveness of treatment and the absence of side effects. Physiotherapy is carried out in special individual booths, separated from each other by screens.
- The patient should take a comfortable position.
- Place your feet on a rubberized mat.
- The skin at the site where the electrodes are applied should be clean, free of bleeding and purulent wounds and metal objects (bracelets, piercings).
- Position the plates of the device, focusing on the doctor’s prescription. The distance between them should correspond to their diameter. If this condition is not met, an increase in the magnetic field is observed, leading to burns.
- It is also important to leave a cushion of air between the electrode and the patient's skin. Its size depends on the method of staging and diagnosis. For example, with deep lesions, the size of the air gap ranges from 2 to 4 cm, and with superficial lesions, no more than 1 cm. For this purpose, special pads made of porous material (felt, felt) are applied to the surface of the human body. It is also not uncommon for the air space between the first and second electrode to be different.
- Make sure the device is grounded, turn it on, set the required power.
- Explain to the patient that mild or severe thermal sensations are possible. But if the heating increases, the patient should urgently inform the nurse about this.
- After the designated time has passed, turn off the power indicator first, and then the voltage.
- Disconnect the electrodes.
- After the procedure, the patient does not immediately leave the physical therapy booth. You are given up to half an hour to rest.
Plates in contact with the human body must be treated with a solution of chloramine (3%) or alcohol (70%).
UHF therapy is carried out daily or every other day, depending on the need and workload of the physiotherapy room. The course of treatment can last up to two weeks for adults and 10-12 days for children.
Possible complications
Physiotherapeutic methods of therapy traditionally differ high level safety for patients. Side effects that periodically occur in patients are associated with incorrect determination of indications and contraindications for treatment methods, or with attempts to independently conduct physical therapy without contacting the attending physician. The following complications are possible:
- redness and irritation of the skin where electrodes are applied to the skin, for example, during electrophoresis with the use of drugs;
- dryness and burning of mucous membranes after UV irradiation;
- allergic reactions or signs of individual intolerance to medications.
If any unwanted reactions occur, the procedure should be stopped immediately. The attending physician conducts an additional examination aimed at identifying the causes of unpleasant symptoms. If they are associated with ongoing physiotherapy, then this procedure is abandoned in favor of its analogues.

Physiotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of chronic bronchitis and its exacerbations in adults and children. A large number of Different methods of influencing the body allows you to choose the most effective type of physical treatment, which allows you to speed up the onset of recovery and improve the future prognosis for the sick person. It is important to note that any therapy methods should be prescribed only after consultation with the attending physician, who examines the patient and determines his indications and contraindications for the procedures.
Application of physical therapy

The use of physiotherapeutic procedures is based on the ability of certain physical factors to provide a therapeutic effect for tracheobronchitis. Moreover, all methods of physiotherapy have scientific evidence of their effectiveness, which allows them to be used in patients of any age and at various stages of therapy.
Physiotherapy – an important part therapy for diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, which makes it possible to have multiple effects on the pathological focus and speed up the recovery of the sick person.
The following effects of physiotherapy have been well studied:
- anti-inflammatory effect associated with inhibition of the formation and release of inflammatory mediators;
- improvement of microcirculation in the area of inflammation, which improves the general condition of the tissue and promotes rapid recovery;
- analgesic effect observed with electrophoresis and ultrasound methods of physiotherapy;
- general tonic effect on the body.
It is important to note that the range of positive effects from these procedures is almost limitless, since when using medicinal electrophoresis, the doctor can use a wide range of medications (Eufillin, Calcium Chloride, etc.) that have their own mechanisms of action.
In clinical practice, for bronchial inflammation in a hospital or at home, the following types of exposure are used:
- therapeutic chest massage;

- electrophoresis with various medications;
- UV irradiation of mucous membranes;
- inhalation;
- magnetotherapy.
The choice of a specific procedure is made by the attending physician based on the indications and contraindications identified in the patient. It must be said that in acute bronchitis the use of physiotherapy methods is quite limited due to the possible negative impact galvanization or magnetic therapy on the pathological focus and increased symptoms of the disease.
Advantages and disadvantages

Comparing the advantages and disadvantages of any treatment method allows you to make the right decision about the advisability of a particular therapy. Exposure to ultra-high-frequency currents is characterized by a number of advantages:
- A large number of indications for use.
- Therapeutic effect without the use of medications.
- Short duration of the procedure.
- Lack of invasiveness and pain during treatment.
- Possibility of use in children.
- Excellent effect in the treatment of joint diseases and inflammatory pathologies.
The method also has quite a few disadvantages. They need to be considered not only by the patient, but also by the doctor. The main disadvantages include:
- Inability to use at home.
- The presence of a number of contraindications, including any trimester of pregnancy.
- Possibility of developing side effects and burns if used incorrectly.
- High risk of connective tissue proliferation in areas of injury.
- Impossibility of long-term use - course mode of application.
These features do not allow UHF therapy to become a widespread method of treating inflammatory diseases. However, in certain situations, this procedure can significantly alleviate the health condition.
It can be useful:
- Which sanatoriums treat joints?
- Surgery to remove a herniated disc: indications and consequences
- Alkaline mineral water for gout
- What is detensor therapy for the spine?
- Stone massage and stone therapy, what is it?
Carrying out physical procedures
Any methods of physiotherapeutic treatment (warming, use of a quartz lamp, etc.) are performed on patients only if there are indications:
- chronic upper respiratory tract infections during remission;
- acute bronchitis or exacerbation of chronic bronchitis for certain methods of physiotherapy, for example, for medicinal electrophoresis with Eufillin in case of bronchial obstruction;
- viscous sputum, leading to significant patient discomfort and respiratory problems.
In addition to the indications, it is important to consider contraindications that limit the use of physiotherapeutic procedures in patients of any age:
- malignant neoplasms;
- pregnancy period;
- acute period of infectious lesions of any localization;
- increase in body temperature.

In all of these cases, physical influence on the human body should be abandoned, as this may cause the development of undesirable effects.
Drug electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is one of the most common methods of physiotherapy for acute and chronic bronchitis. The biological effect of the procedure is associated with two types of effects: galvanization and the direct action of the medications used. Galvanization is the effect of electric current on biological tissues, expressed in the form of an anti-inflammatory effect, as well as improved metabolism and regeneration.
When selecting medications for medicinal electrophoresis, it is very important to exclude the patient’s allergy to these medications, since otherwise severe side effects may develop.

To carry out the procedure, various medications are used to achieve a complex effect on the pathology. Most often, electrophoresis is performed with the following medications:
- calcium chloride, which makes it possible to transform sputum into a more liquid state, as a result of which the patient can cough more easily and expectorate mucus from the bronchial tree;
- the use of Eufillin is indicated for obstructive bronchitis, when bronchospasm and difficulty breathing are observed, it provides relaxation of smooth muscle cells, eliminates symptoms of respiratory failure and improves the general condition of the patient;
- the use of potassium iodide can reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process in the bronchial wall, as well as inhibit the growth of bacterial microorganisms, which has a positive effect on the course of the disease;
- in case of chronic bronchitis, electrophoresis with Lidase is most effective, allowing to restore the patency of the bronchial tree.

The use of these medications makes it possible to improve the general well-being of the patient, alleviate existing symptoms and ensure a faster onset of recovery for a person with acute and chronic bronchitis. It should be noted that the choice of a specific drug, as well as its dosage and volume, is made only by the attending physician based on the patient’s examination data. This is due to the fact that each of the drugs has its own indications and contraindications for use, and therefore may be either ineffective or unsafe for a particular patient.
Therapeutic effects of the procedure
For several decades, many chronic and convalescent diseases have been treated with UHF. What it is is known not only to those who often suffer from otitis media, bronchitis or sinusitis. This procedure is used for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal diseases. Under the influence of ultrahigh frequencies, the following processes occur in the body:
The number of pathogenic bacteria decreases;
The number of leukocytes increases and their effect increases;
Blood circulation improves;
The immune system is activated and the body’s protective functions are increased;
Capillaries dilate and vascular tone decreases;
Metabolism improves and intestinal motor function is stimulated;
Smooth muscle spasms are relieved;
Improves the flow of mucus during sinusitis or bronchitis;
Swelling goes away and inflammation decreases;
Pain sensations are reduced;
The person relaxes and calms down.
Safety rules and special instructions
Responsibility for compliance with safety rules falls on the shoulders of the doctor involved in treatment. But just in case, it will also be useful for the patient to know these rules:
- Procedures are always carried out in specially equipped rooms where screened barriers are created.
- The patient must be at a safe distance from the device. This means that for a while it is important to prevent human contact with any metal objects and electrical power cords of the device.
- Before using the UHF drug, the physician must check the integrity of all wires (power supply, electrodes, etc.). If breaks or damage to the insulating layer on the wires or electrodes are detected, the procedure is impossible.
- Particular care is required when treating pneumonia and other severe inflammatory processes, as they are accompanied by connective tissue formations. The duration of the procedure in such cases is reduced.
- In cases where metal implants smaller than 2 centimeters are installed in the human body, UHF is applied for only 5–10 minutes.
When is a UHF device used?
High frequency facial treatment is used by estheticians to treat and prevent acne, reduce enlarged pores and the appearance of fine lines/wrinkles. The device can also stimulate collagen, elastin and improve cell turnover. High frequency treatment can counter puffy eyes and dark circles under the eyes.
A professional facial uses a machine that delivers alternating current and produces a thermal effect to help stimulate blood circulation. The UHF device increases cell metabolism, improves oxygenation and absorption of skin care products, and exfoliates dead cells.
Its action is classified as antiseptic (it can coagulate and heal open wounds on the body, thereby preventing infections). The primary effect of high-frequency current is thermal (heat generation) and is characterized by high oscillation speed. Because of fast speed The high frequency oscillations do not cause muscle contractions - instead it works on the principle of toning the skin.

The device is also indispensable in the treatment of the following diseases:
- acute inflammatory diseases;
- chronic diseases;
- purulent diseases;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- polio (in the early stages);
- ulcers, wounds;
- frostbite of any degree.
What is UHF
The abbreviation UHF stands for ultra-high frequency therapy. This is one of the methods of physiotherapeutic influence on humans in order to combat diseases.
The physiotherapy procedure involves the use of ultra-high frequency electromagnetic fields that freely penetrate through solid matter, affecting the tissues of the body. If we ignore complex terminology, the technique is based on thermal action. Due to the influence of the electromagnetic field that the equipment emits, not only tissues are affected, but even internal organs.
The main advantage of the UHF procedure is its complete painlessness. Moreover, the use of electromagnetic waves is appropriate on any part of the body and even with pathologies such as fresh fractures or active inflammation, no matter how deep they are.
The concept of UHF treatment, indications, limitations, physical action

UHF therapy (interpretation: ultra-high-frequency therapy) is a technique in which tissue is warmed by high-frequency electromagnetic pulses. In Germany in 1929, electromagnetic fields with very high frequencies began to be used as a therapeutic physiotherapy procedure. The study of the effects of UHF radiation began after workers at radio stations began to complain of discomfort and pain from the influence of radio wave radiation.
UHF can be used to treat pathologies respiratory organs, ENT pathologies, heart and vascular diseases, digestive tract, urinary system, genital pathologies, skin diseases. Treatment is indicated for patients with diseases of the nervous system and musculoskeletal system. UHF can be used for pathologies of the visual analyzer, dental diseases, and also after surgical treatment. UHF can be prescribed to children and newborns.
The main effects of ultrahigh frequency radiation:
- Oscillatory effect (physical, chemical and molecular changes are triggered in cellular structures, metabolic processes increase, and the rate of chemical reactions accelerates).
- Thermal effect (tissues are heated due to the transition of magnetic radiation into heat, the temperature at the site of exposure rises).
A technique that is allowed in the presence of inflammation is UHF therapy. During inflammation, an infiltrate (accumulation of blood and lymphatic fluid) is formed. When treatment is carried out at the site of the inflammatory focus, blood circulation is activated and the outflow of lymphatic fluid is accelerated. At the same time, the infiltration begins to resolve. During therapy, calcium ions accumulate in inflamed tissues. They promote the appearance of connective tissue cords in the area of inflammation, which prevent the spread of infectious agents in the blood, as well as into surrounding tissues. UHF is performed only if the inflammatory and purulent discharge can flow out through the drainage. If this condition is not met, treatment is prohibited.
The mechanism of UHF in different diseases may differ.

In case of pathologies of the respiratory system and ENT diseases (pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis, tonsillitis), electromagnetic radiation helps reduce the growth and development of microorganisms. Rhinitis relieves nasal congestion. During the physical procedure, pain is reduced and local and general immunity is strengthened. Improved regeneration is observed in tissues. The use of physiotherapy prevents the complicated course of diseases.
In diseases of the heart and blood vessels, electromagnetic radiation expands the walls of the vascular bed. This leads to an acceleration of blood flow in the periphery, as well as in the heart vessels and lung tissue. The heart muscle begins to receive more blood. The walls of the vessels are strengthened, which leads to normalization of pressure. During treatment, cardiac edema in the periphery, especially in the lower extremities, goes away.
In patients with pathologies of the digestive tract, general immunity increases. Often with gastritis, ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract, pancreatitis, colitis, patients experience severe pain. UHF treatment helps reduce pain. During therapy, inflammation decreases and regenerative processes in the cells of the intestinal tube, liver, and pancreas are accelerated.
Physiotherapy relieves spasms of the stomach and gallbladder muscles. The therapy accelerates the contraction of the intestinal walls, which promotes normal digestion and reduces the likelihood of constipation. When bile secretion stagnates, treatment helps improve the flow of bile through the ducts.
For pathologies of the urinary system, inflammation goes away during treatment and tissue swelling decreases. UHF allows you to accelerate blood flow in the kidneys, which increases diuresis. Electromagnetic radiation increases the regeneration of kidney and bladder tissue. With regular courses of therapy, patients experience longer remission (the condition is not exacerbating), and the disease progresses in a milder form.
In patients with skin pathology, the prescription of therapy prevents suppuration from developing at the site of the lesion. When adding bacterial flora, UHF helps reduce the growth and reproduction of microbes. When exposed to electromagnetic radiation, lymphocytes, mast cells, and phagocytes begin to work intensively in the skin. They reduce inflammation and fight bacterial agents.
Radiation acting on the skin increases blood flow to the affected areas of the skin. This leads to increased formation of new epithelial cells. If the skin pathology is of an allergic nature (psoriasis, streptoderma, atopic dermatitis, eczematous rashes), then the treatment provides an antiallergic effect.

For pathologies of the nervous system (neuritis, neuralgia, migraine headaches, sciatica, encephalitis, head and spinal cord injuries), therapy relieves pain. This occurs due to a slowdown in the transmission of nerve impulses along nerve fibers. During therapy, the tone of the vascular walls is normalized, which reduces the intensity of migraine headaches. Blood flow increases in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, which stimulates the restoration of nerve cells.
When performing UHF in patients with pathologies of the motor system (radiculopathies, fractures, osteochondrosis, dislocations, arthritis, osteomyelitis), blood flow accelerates in the affected area. The treatment has a positive effect on the development of collateral circulation, when direct blood flow is impossible. The blood begins to enrich the damaged joint or bone with microelements, which accelerates tissue recovery.
Physiotherapy is actively prescribed for pathology of the visual organ and its auxiliary elements. During the course of treatment, blood flow in the eyeball, eye muscles, and eyelids increases. Electromagnetic radiation relieves the inflammatory reaction and provides an antiallergic effect. When conducting UHF in the tissues of the visual organ, the formation of phagocytes increases, which fight bacterial agents in case of infection. Under the influence of UHF, the regenerative function of the cells of the organ of vision increases.
UHF is often prescribed for diseases of the teeth and gums. Against the background of physical therapy, blood flow in the gums improves, the reproduction and activity of bacterial agents decreases. When using UHF, the intensity of the pain syndrome decreases.
One of the few physiotherapy procedures allowed after surgical treatment is UHF.
The technique is prescribed to patients after operations and acute conditions to speed up recovery processes. When using physical therapy, blood flow in small vessels increases and bypass vessels are formed. This helps accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue in the suture area. Physiotherapy helps prevent the addition of pathogenic bacterial flora after surgical treatment. UHF increases overall immune defense and relieves pain. The use of UHF makes it possible to reduce the duration of rehabilitation.
Indications and limitations for the use of UHF therapy, undesirable manifestations
UHF treatment has its indications and limitations. When prescribing physiotherapy, the doctor must take them into account. Before using therapy, you need to pay attention to the patient’s age, the severity of the pathology, and chronic diseases.
Indications for physiotherapy:
- Autoimmune, infectious and other pathologies of the skin (psoriatic skin lesions, burns, dermatitis, streptoderma, purulent lesions, herpetic eruptions, eczema, neurodermatitis, acne, panaritium, frostbite, ulcerative defects, bedsores).
- Respiratory diseases and ENT pathologies (inflammation of the lungs, bronchi, pleura, runny nose, tonsillitis, inflammation of the maxillary and frontal sinuses, laryngitis, diseases of the auditory organ).
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system (bursitis, rheumatic diseases, radiculopathy, fractures, dislocations, osteochondrosis).
- Pathologies of the nervous system (depressive disorders, cognitive impairment, autonomic dysfunction, neuritis, spinal cord pathologies, neuralgia, migraine headaches, head injuries, poor sleep).
- Diseases of the digestive tract (gastritis, ulcerative lesions of the digestive tube, pathologies of the pancreas, liver, gall bladder, constipation, colitis).
- Diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems (pyelonephritis, cystitis, inflammatory pathologies of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, prostate gland, endometritis, fungal infection of the genital tract, mycoplasma infection).
- Dental pathologies (gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontal inflammation, injuries of the maxillofacial skeleton).
- Recovery after surgical treatment and acute illnesses.

UHF is not recommended for patients with pathologies of the coagulation system, severe hypertension, or malignant tumors. The use of UHF is prohibited in case of hyperthermia or the presence of an artificial pacemaker. The procedure should not be performed in case of ischemic damage to the heart muscle, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris in the stage of decompensation, or venous thrombosis. Physiotherapy is not used during pregnancy. Relative restrictions are considered: benign neoplasms, hyperthyroidism, the presence of prostheses, fragments and other metal objects (since a magnetic field is applied that can move foreign bodies).
The therapeutic effect is influenced by a number of factors:
- The severity of the pathological condition.
- The range of radiation fluctuations (the intensity of the magnetic field and current must be dosed for a specific patient), the depth of wave penetration.
- Duration of UHF treatment.
- Location of emitters.
- Use of other therapy methods.
- The patient's sensitivity to the physiological effects of current.
There are no serious consequences when UHF treatment is carried out correctly. If safety rules have been violated, burns, bleeding, and scars may occur. Sometimes the patient may receive an electric shock. Burns usually occur when a damp cloth pad is used or when the skin comes into contact with the emitter plate. Bleeding is likely in patients with a disorder of the blood coagulation system or cancer pathology. The appearance of a scar is possible during treatment after abdominal surgery. Electric shock can occur if therapy is carried out incorrectly, when the patient touches exposed elements. This complication is very rare.
How to prepare for the procedure
The treatment procedure for this therapy is prescribed by the attending physician. At the same time, he must indicate the method, type of device and its power, the diameter of the treatment plates, the protective effect, the value of the air gap, the duration of treatment, frequency, and the number of procedures for complete recovery (or per course). The procedure itself is carried out by a physiotherapist, preferably an experienced specialist, since radiation is a serious therapy that can either help the patient or harm if treated incorrectly. That is, the first thing you need is to choose a qualified doctor. Secondly, do not forget to warn about the presence of metal implants. Third, listen to your own feelings. Usually the procedure lasts no more than fifteen minutes. During the session you should not experience severe discomfort or acute pain. If you feel too hot, you should ask your physiotherapist to stop the procedure. This may mean that your doctor has given you the wrong amperage, or that you are too sensitive to this treatment method. Further actions must be discussed with a physiotherapist.
UHF therapy is effective way eliminating many diseases, including chronic ones, in the shortest possible period of time. What has been bothering you for many years will no longer remind you of itself after treatment. Just 6-10 procedures guarantee, if not complete recovery, then a significant improvement in health. In the absence of any kind of contraindications, UHF has a beneficial effect on the patient’s immunity and general well-being. It is important to remember that the best option is treatment under the supervision of a qualified physician. Only in this way can you achieve a positive effect in the shortest possible time.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
Method of application - placement of electrodes
There are three possible ways to place electrodes on the affected area.
- Longitudinal. It is used to warm up superficial lesions. The electrodes are placed on only one side of the body.
- Transverse. Unlike longitudinal, the electrodes are located opposite each other in such a way that one is directed to the painful area, and the other is located on the opposite side of the body.
- Tangential arrangement implies both electrodes on the same plane, but at a distance from each other. The electromagnetic field thus passes in an arc between the two plates.
UHF therapy is a complex treatment method that uses an alternating electric field of ultra-high frequency (UHF), supplied to problem areas of the patient’s body using capacitor plates. When carrying out UHF therapy procedures, they use such devices as UHF-30, UHF-66, “Ekran-1”, UHF 8-30 “Undaterm” (a universal medium-power device that acts using a capacitor technique, an induction cable and a tuned circuit) , stationary device "Ekran-2". The specified devices (portable and stationary) are connected to an alternating current network with a voltage of 220 V or 127 V. Electrical diagram these devices consist of power transformer, one circuit, which is inductively connected to a therapeutic device that has capacitor plates - electrodes, through which the patient’s problem (pathological foci) areas are exposed to a pulsed ultra-high frequency field.
Capacitor electrode plates are:
Small disc metal plates coated with insulating material (plastic, rubber, plexiglass);
Flexible soft rectangular plates with an area of 150, 300 and 600 cm 2.
Methods and techniques for conducting UHF therapy procedures
The procedure is carried out using two capacitor plates, which are placed transversely, longitudinally or at an angle relative to the surface of the body, and the distance between them must be at least the diameter of the plate, otherwise an increase in field strength and overheating of the patient’s skin may occur (up to before the burn). In the case when the capacitor electrode plates are located transversely, the electric field lines that arise when the device is turned on penetrate the entire thickness of the source of influence on the patient’s body. This technique is used when the lesion is located deep (pathological).
In another case, when the pathological focus is on the surface of the patient’s body, capacitor electrode plates are installed longitudinally. According to this technique, the electric field lines are located superficially, but cover the pathological focus to a small depth, without penetrating deeply.
In medical practice, the first method with a transverse arrangement of capacitor plates is most often used.
When carrying out UHF therapy procedures, the following condition must be observed: an air gap is left between the electrode plate and the surface of the patient’s body, the size of which is determined by the depth of the pathological focus. For example, with a superficial location of the lesion, the air gap is set to 0.5-1 cm, and with a deep location - from 2 to 4 cm. In this case, the total gap size under both plates should not exceed 6 cm when using portable devices. In addition, the air gap must be kept unchanged throughout the procedure. This is achieved by using special pads made of perforated (i.e. with small holes) felt or felt of a certain thickness.
When conducting UHF procedures for children and adolescents, these pads are fixed on electrode plates; the same is done when using flexible soft electrodes.
When performing UHF procedures, the following condition is observed: the air gap between one of the plate electrodes and the pathological focus should be minimal - from 2 to 1 cm, and the gap under the other electrode should be large, but not more than 4 cm. For example, with pneumonia of the posterior segment of the lower lobes of the lung on the right, the electrode plate is placed in front with an air gap of 4 cm, and in the back - 2 cm.
Depending on the size of the pathological focus, electrode plates No. 1, 2 or 3 are used during UHF procedures.
When performing UHF procedures, the effect of the electric field on the lesion (pathological) is dosed according to the output power of the corresponding device, according to the patient’s thermal sensations, and also according to the time of exposure.
In the medical practice of UHF procedures, based on sensations, patients distinguish between doses: athermic, oligothermic and thermal. With an athermic dose, heat generation in the pathological focus is insignificant, therefore it is not perceived by thermal receptors of the skin, and as a result, the patient does not experience a feeling of warmth. To obtain athermic and oligothermic doses during UHF procedures, the lowest output power of the corresponding device is usually used. In the case where the patient notices a feeling of intense heat, increase the air gap within acceptable limits.
Reduce the thermal dose by disrupting resonance, focusing on the weak glow of a neon light bulb placed in electric field UHF, not recommended.
The instructions of the Ministry of Health of Russia have established that exposure to a UHF electric field in adults in the area of the face and neck is carried out at a current power of 20-30-40 W, in the area of the chest, abdominal organs and small gases - at 70-80-100 W, on small joints of the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders - 30-40 W, ankles, knees, hip joints- 70-80-100 W.
When conducting UHF procedures in children and adolescents, the power of exposure is set depending on age. For example, when exposed to a UHF electric field, 15-20-30 W is set in the face and neck area, 30-40-70 W in the chest and abdominal areas, and 30-40-70 W in the upper and lower limbs- 15-20-30-40 W. To maintain a constant air gap during UHF therapy procedures in children and adolescents, felt or flannel circles with a thickness of 1, 2, 3 cm are placed between the electrode plates and the surface of the body, depending on the air gap.
The procedure is carried out daily, but sometimes every other day. For the entire course of UHF therapy treatment, from 5 to 15 procedures are prescribed for adults and from 4 to 12 for children.
The mechanism of action of the UHF field is relatively complex and is expressed in the oscillatory movements of charged particles with subsequent physical and chemical changes in the cellular and molecular structure of tissues in the area of influence on the patient’s pathological focus. As a result of processes occurring in superficial and deep tissues under the influence of a UHF field, heat is released with different intensities, depending on the power of the current supplied to the electrode plates. At the same time, the use of a UHF field in a non-thermal dosage according to methods approved by the Russian Ministry of Health has a pronounced oscillatory effect. It is almost impossible to isolate thermal and oscillatory effects, therefore, the responses of the patient’s body when exposed to pathological foci are associated with the total effect of the UHF electric field, but with some procedures it is possible to create the advantage of thermal or oscillatory action.
Conducted in the USSR in the 1970-1980s. Special clinical studies have reliably established that the UHF electric field, when carrying out appropriate procedures, has the following effects:
Increased blood and lymph circulation in the pathological focus;
Dehydration of inflamed tissues;
Stimulating the functions of the reticuloendothelial system, increasing the activity and intensity of phagocytosis;
A noticeable increase in the number of calcium ions at the site of inflammation;
Reducing the vital activity of pathogenic bacteria, slowing down the absorption of toxic products from the source of inflammation;
Strengthening the processes of formation of a protective barrier from connective tissue elements;
Antispastic effect on the smooth muscles of the stomach, intestines, gall bladder;
Noticeable stimulation of bile secretion;
A certain decrease in the secretion of the bronchial glands, acceleration of the regeneration of nerve elements in inflammatory, degenerative and traumatic injuries;
Dilatation of capillaries, arterioles;
Acceleration of blood flow in the pathological focus;
Reducing high blood pressure (bradycardia often occurs);
Increase in glomerular filtration;
Increased blood flow in the kidney area.
The above studies have scientifically substantiated the following indications for the use of UHF therapy:
Acute inflammatory processes in organs and systems;
Spinal cord and peripheral nerve injury;
Radiculitis;
Neuralgia;
Polio;
Encephalitis;
Myelitis during periods of subacute and chronic course;
Raynaud's disease;
Obliterating endarteritis;
Acute and subacute inflammation of the uterus and appendages.
Studies conducted in specialized clinics have identified the following contraindications:
Malignant neoplasms;
Systemic blood diseases;
Heart failure of II-III degree;
Aortic aneurysm;
Hypotension (persistent low blood pressure);
Tendency to bleeding;